Layered Security: Strengthen Your Cyber Defenses the Smart Way
It is hard to imagine a discussion on cybersecurity measures without eventually running into the layered security approach to cyber defense. Layered security is a strategy that employs multiple levels of security to safeguard organizational digital assets from various types of threats. Rather than relying solely on a singular defense method, this approach combines different measures to create multiple barriers to stop potential intruders at different points in a system.
What Is Layered Security?
Layered security, or defense in depth, is a cybersecurity approach that utilizes multiple layers of defense to protect sensitive information from a wide range of threats. This security measure has been around for quite some time and has evolved alongside other cybersecurity measures. A multi-layered approach is vital because it provides redundancy. If one layer is compromised, other defenses continue to protect the system, ensuring that an attack doesn’t succeed. This is especially critical in an era where cyber threats are and will continue to become increasingly sophisticated and diverse, ranging from malware and phishing attacks to more complex Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). By addressing vulnerabilities at various levels, organizations enhance their ability to detect and mitigate risks early before they can cause significant damage.
One thing that people should understand about layered security is that it is more of a catch-all, broad spectrum blanket than a cure to a specific problem. Whether defending against malicious software, unauthorized access, or user error, this model provides robust protection for all areas of the business, including data, applications, and network infrastructure. As cyberattack methods evolve, relying on a single security solution is no longer sufficient. A layered strategy ensures a more comprehensive defense system that adapts to a wide range of attack methods.
Also read: 5 Step-Guide to Complete Remote Work Security
Key Pillars to Focus on While Implementing Layered Security
- Critical Applications: Securing your most vital business applications is essential in any layered security strategy. These applications often contain the most sensitive data and are prime targets for cybercriminals. Utilizing secure hosting services that store data in high-security data centers (SSAE/SOC certification) can provide an added layer of protection. Strong access controls and application-level security configurations should be in place to prevent unauthorized access to these critical systems, ensuring they operate securely and remain resilient to threats.
- Email: Email continues to be one of the most significant entry points for cyber threats. Implementing robust security services to monitor and safeguard against email-based attacks, such as phishing, malware, and business email compromise (BEC), is essential. Solutions such as email filtering, spam protection, and advanced threat detection can minimize the risk of malicious emails infiltrating the system. Additionally, organizations should enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for email accounts, adding another layer of protection.
- Devices: Modern workplaces rely heavily on personal and corporate devices, making them a prime target for cyberattacks. Protecting devices, including desktops, laptops, mobile phones, and tablets, is critical. Advanced threat detection tools and continuous monitoring ensure that any unusual behavior on a device is quickly identified. It’s essential to implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, like MS Defender for Endpoint, which provide proactive monitoring and remediation, going beyond traditional antivirus software.
- Employee Training: Employees are often the first line of defense against cybersecurity threats, making ongoing security awareness training a critical component of your security strategy. Regular training helps staff recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other malicious activities. Teaching employees about safe password practices, data privacy, and the latest cyber threats can significantly reduce the chances of human error leading to a security breach.
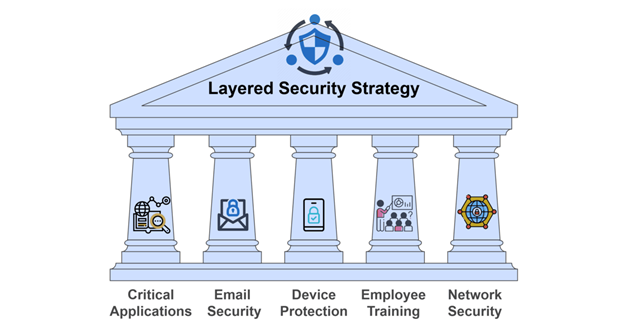
- Network Security: A robust network security framework is essential for any organization. This includes the implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems to block unauthorized access to the network. Network segmentation further enhances security by limiting the spread of potential threats, ensuring that sensitive data and systems are isolated from less critical areas of the network.
- Data Security: Protecting data at rest and in transit is crucial in safeguarding sensitive information. Data encryption is a fundamental part of any security strategy, ensuring that even if attackers intercept data, it remains unreadable. Strong encryption protocols for both stored data (e.g., database encryption) and data in transit (e.g., SSL/TLS for web communications) help protect information from unauthorized access and potential theft.
- Access Control: Limiting who can access what within an organization is vital for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that employees and users are granted the minimum necessary permissions based on their roles within the company. Along with RBAC, implementing proper authentication mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA) helps secure user accounts and reduces the risk of compromised credentials. Regularly reviewing access privileges and adjusting them as necessary is also essential to ensure security is maintained.
Direct Layered Security Approaches
Implementing direct layered security approaches is essential for businesses to stay ahead of cyber threats and minimize risk. These specific security tools and strategies enhance your defense mechanisms, offering additional barriers to protect your critical data and infrastructure. Below are some of the most effective approaches:
- Antivirus and Antimalware Software: These foundational tools are crucial for detecting, preventing, and removing harmful software such as viruses, ransomware, and spyware. Antivirus software scans for known threats and can prevent them from infecting your system, while antimalware focuses on identifying more advanced and evolving malicious software. Both are essential for securing endpoints and ensuring that your systems remain protected against a wide range of cyberattacks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA strengthens access control by requiring users to provide additional verification factors beyond just a username and password. This could involve something they know (like a PIN), something they have (like a smartphone app or hardware token), or something they are (such as biometrics). With MFA in place, even if an attacker acquires a user’s credentials, they won’t be able to access the system without the second form of authentication, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external sources of traffic, including the internet. They monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access and can block malicious traffic such as DDoS attacks or attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in your network. Their role is to filter data packets and ensure that only safe traffic is allowed into your network.
- Encryption: Encryption transforms sensitive data into unreadable ciphertext, ensuring that only authorized users with the decryption key can access it. By encrypting data both in transit (during transmission) and at rest (when stored), you protect it from unauthorized interception, theft, or tampering. Encryption is a critical layer in protecting customer information, intellectual property, and other sensitive assets, especially when dealing with compliance requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools provide continuous monitoring and advanced threat detection for all devices connected to your network, including computers, mobile devices, and IoT devices. Unlike traditional antivirus solutions, EDR solutions are designed to detect complex, unknown threats and provide detailed insights into security incidents. EDR continuously monitors endpoints for signs of malicious activity, investigates suspicious behaviors, and responds automatically or manually to mitigate potential risks.
Also read: Optimizing Endpoint Device Management with Microsoft Intune
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions aggregate, analyze, and store security event data from across your network and applications. By providing real-time visibility into security alerts and events, SIEM helps detect and respond to threats faster. SIEM platforms analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential security incidents and provide insights into unusual activities that might indicate an attack. This allows for more proactive monitoring and quicker responses to emerging threats.
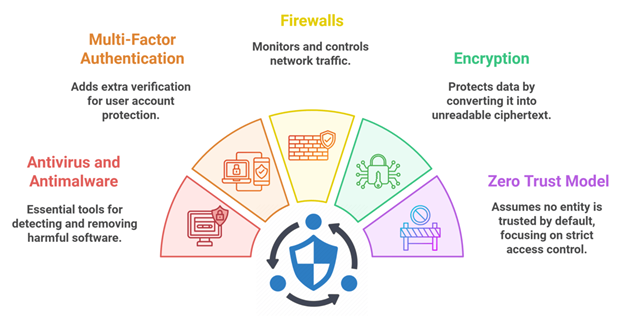
- Zero Trust Security Model: The Zero Trust model operates on the principle that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Every access request must be thoroughly authenticated, authorized, and continuously monitored before being granted. This security approach enforces strict access control policies based on the least privilege principle, ensuring that users and devices only have access to the resources they need. Zero Trust minimizes the risk of breaches by assuming potential threats could come from anywhere, including internal users and compromised devices.
Also read: Navigating Zero Trust Security: Concepts, Standards, and Applications
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC is a system for managing access to critical resources based on the roles assigned to individual users within an organization. It ensures that users only have access to the information and systems necessary for their job functions. By limiting access based on roles, organizations reduce the likelihood of unauthorized users accessing sensitive data, whether intentionally or accidentally. RBAC is particularly useful for large organizations that need to manage complex user permissions and enforce strict security measures across departments or teams.
These direct security approaches each play a vital role in creating a robust, multi-layered defense strategy. By combining them, organizations can protect against a wide range of cyber threats, from unauthorized access and data breaches to advanced persistent attacks and malware infections.
Overcoming Barriers to Implementing Layered Security
-
Cost Considerations and Solutions
Layered security can seem expensive, but options like managed security services and cloud-based solutions help reduce costs. Bundled security packages offer affordable, comprehensive coverage for smaller businesses. Cloud security providers typically offer scalable, pay-as-you-go pricing. Managed services deliver enterprise-grade security without hefty upfront costs.
-
Limited Expertise and the Benefits of Outsourcing
Outsourcing to experts like Apps4Rent can provide access to top-tier security professionals. Managed service providers handle 24/7 monitoring and incident response. Outsourcing reduces the need to hire in-house security staff, saving on recruitment and training. MSSPs offer the expertise to manage and maintain a layered security strategy effectively.
-
Complexity of Managing Multiple Layers
Centralized management tools streamline monitoring of all security layers from one interface. Automated systems help detect and respond to threats proactively, reducing manual intervention. Ensuring compatibility between security tools is essential for reducing complexity. Consulting with a provider helps ensure smooth integration and management.
-
Misconceptions About the Need for Comprehensive Security
Cybersecurity is crucial for businesses of all sizes, not just large enterprises. A comprehensive security strategy can be scaled to fit any organization’s needs and budget. Layered security adapts to new threats and vulnerabilities, making it an ongoing process. Small businesses are frequent targets of cybercriminals and need robust protection too.
Elevate Your Security with a Layered Approach
Looking to strengthen your organization’s defenses? Implementing a layered security strategy is an essential step to safeguarding your critical resources from various cyber threats. At Apps4Rent, we specialize in helping businesses adopt a robust, multi-layered security framework that provides comprehensive protection across all digital assets. Our cloud experts guide you through implementing effective layered security, incorporating tools like Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for proactive threat detection and response.
Start Securing with Apps4Rent Today
Stay protected against evolving cyber risks with a layered security strategy. Connect with Apps4Rent for guidance on implementing this essential security approach. With our dedicated support and expertise, you can build a resilient defense system that safeguards your assets from every angle. Contact us to get started on enhancing your layered security measures today.





